Network Diagram & Setup
Create a network diagram
Go to Draw.io
I have built this network diagram below for my SOC setup using the ELK stack.
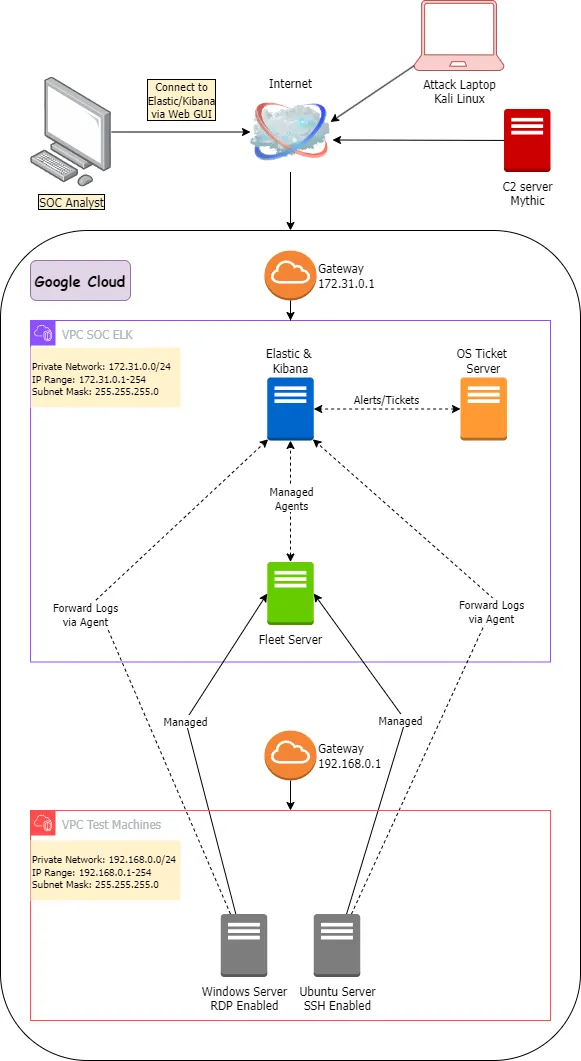
Here, I am intentionally keeping the Windows and the Ubuntu server out of the ELK VPC and in a separate Test Machines VPC so that if someone was to infiltrate these machines they will have restricted access to our internal network. It is more secure this way.
Network Setup
Go to cloud.google.com and setup account
Create a new project: SOC-Monitoring. Edit the project id if needed.
Steps to create VPC Network
From the left-corner hamburger menu:
- Select VPC Network > Enable Compute Engine API
- Create VPC Network
- Name the network (
soc-elk) > Set Subnet creation mode to Custom- Name the subnet (
vpc-internal) > Choose region (asia-east1) > Set IPv4 range (172.31.0.0/24) > Done- Leave all other settings as it is
- Create VPC network
My VPC Configuration
ELK VPC
| Parameter | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Network Name | soc-elk |
| Subnet Name | vpc-internal |
| Region | asia-east1 |
| Subnet IP Range (IPv4) | 172.31.0.0/24 |
| Subnet Creation Mode | Custom |
Test Machines VPC
| Parameter | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Network Name | vpc-test-machines |
| Subnet Name | vpc-test-machines-internal |
| Region | asia-east1 |
| Subnet IP Range (IPv4) | 192.168.0.0/24 |
| Subnet Creation Mode | Custom |
The VPC networks should be in the same region as the virtual machine location. Now we can go ahead with the firewall configuration:
Steps to create firewall rules
Select the VPC network we have just created. Now under the firewall tab:
- Add firewall rule
- Name the rule > Make sure that your network is selected > Priority can be
1000- Select direction of traffic: Ingress/Egress
- Select action: Allow/Deny
- Select targets: All instances in the network if we want all of the instances inside the VPC to have this rule or Specified target tags if we want to have only specific machines to include the rule. In the second case, we’ll need to provide the target tag we want which we will include later while setting up our VMs to specify which machines the firewall rule will be applicable to
- Provide the source/destination IPv4 ranges
- Select specific protocols and ports or we can also Allow all
- Create the rule
My Firewall Configuration
SOC ELK VPC
| Rule Name | Source IP | Destination IP | Targets | Protocol/Port | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
allow-ingress-internal | 172.31.0.0/24 (VPC range) | - | Apply to all | Allow all | Allows internal VPC communication |
allow-egress-internal | - | 172.31.0.0/24 (VPC range) | Apply to all | Allow all | Allows egress traffic within the VPC |
allow-soc-analyst | SOC Analyst machine public IP | - | Apply to all | Allow all | Allows full SOC analyst access to the network |
allow-agent-logs | 192.168.0.0/24 (Test machines subnet) | 172.31.0.2 (internal IP of ELK server), 172.31.0.3 (internal IP of fleet server), <external-ip-elk-server>, <external-ip-fleet-server> | fleet-server, elk-server (Specify network tag) | TCP/8220,9200 | Allows agents to send logs to Fleet Server and Elasticsearch instance |
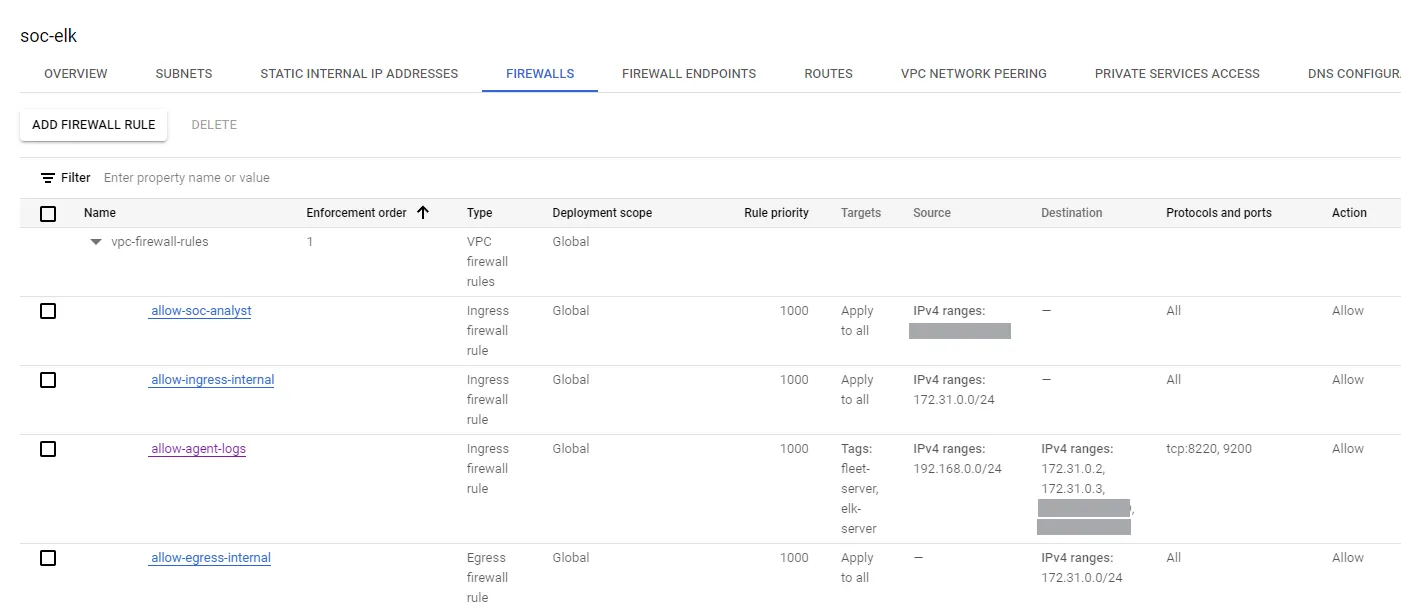
The first two rules allow all internal communication inside the VPC.
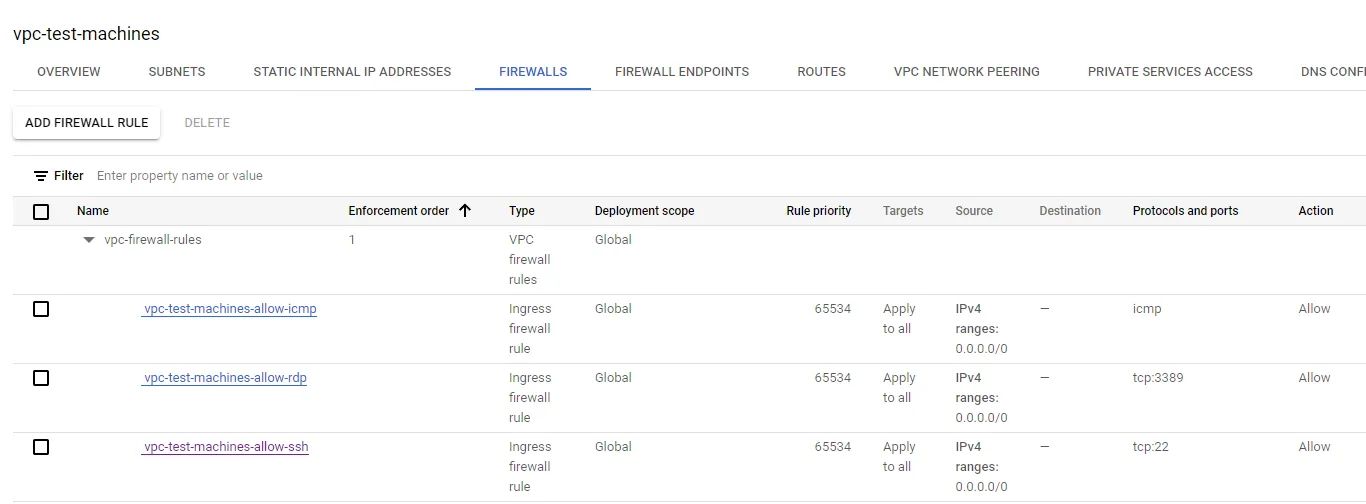
Test Machines VPC
| Rule Name | Source IP | Destination IP | Targets | Protocol/Port | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
vpc-test-machines-allow-icmp | 0.0.0.0/0 | - | Apply to all | icmp | Allows ICMP connection from internet |
vpc-test-machines-allow-rdp | 0.0.0.0/0 | - | Apply to all | tcp:3389 | Allows RDP connection from internet |
vpc-test-machines-allow-ssh | 0.0.0.0/0 | - | Apply to all | tcp:22 | Allows SSH connection from internet |
Additional firewall measures
To increase security:
allow-agent-logs: Instead of192.168.0.0/24, we can specify the exact IPs of the Windows and Ubuntu servers to limit the attack surface. We could create separate rules for each server or update the source IP with the relevant IP addresses.
However, for this project I am going to keep the port 8220 (default port fleet listens on to manage agents) and 9200 (default port elasticsearch listens on for agents) open to the vpc-test-machines-internal subnet to allow them access to our fleet and elasticsearch instances.
VPC network peering
To get logs from the Windows and Ubuntu machines (in the vpc-test-machines) to our ELK setup (in the soc-elk VPC), we need to make sure that the the two VPCs are able to establish connection with each other (with the firewall rules configured properly).
This is where we need VPC network peering between the two networks. With network peering our machines will be able to discover and/or recognize each other’s IP addresses and with the firewall rules set up as above, they will be able to make connections with each other as intended.
- Select VPC Network > VPC network peering
- Create peering connection > Continue
- Name the peering (
soc-elk-to-vpc-test-machines) > Select first VPC (e.g.soc-elk)- Peered VPC network > choose the same project or a different project (I choose the same project)
- Choose second VPC (e.g.
vpc-test-machines)- Leave all other options as it is
- Create peering connection
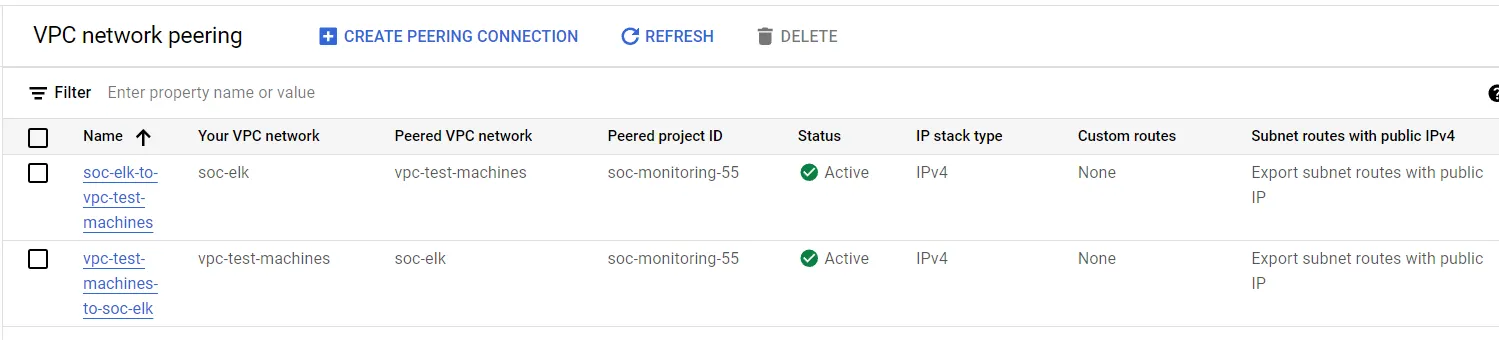
Network peering won’t be active until both the networks are peered with each other. After creating both the peering connections, the Status should be showing as active.