Investigate - Mythic Agent
Objective:
- Learn how to investigate Mythic telemetry
Since I want to investigate a C2 that I performed myself, I already know the service name which is svchost-ucch45.exe. In real-time investigation efforts, one would have to investigate and find out the service name themselves.
Identify C2 services running on the system
One way is through investigating network telemetry. Usually, a C2 session will involve a lot of back and forth traffic. Weighty byte transfers of this type end up being among the top 10 talkers i.e. the top 10 address pairs having the heaviest transfers. In addition to bytes, we can also take a look at heartbeats. One interesting tool to investigate these kinds of evil is RITA(Real Intelligence Threat Analytics) by Black Hills Information Security.
Another way to investigate C2 is to look for process creations and combine it with network creations. Sysmon can be heavily utilized for this scope. Network creations will have an Event ID 3.
Look for suspicious activities
Previously I created a dashboard Suspicious-Activity.
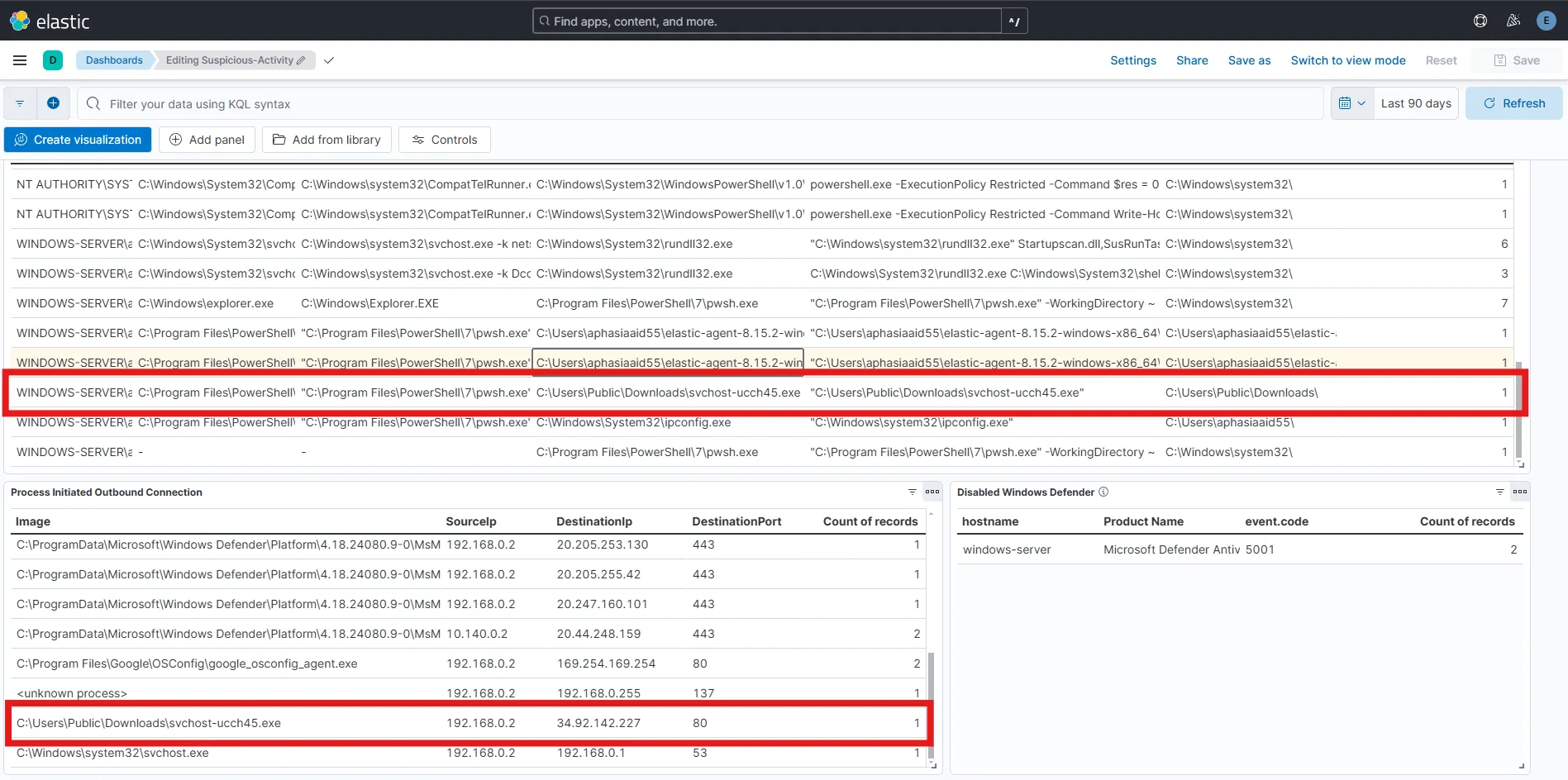
After observing the dashboard, I find one suspicious process creation activity in the C:\Users\Public\Downloads\ directory which is unusual. I can also see that the process with the same name svchost-ucch45.exe from the same local directory, has initiated an outbound connection on port 80. By combining the process creation and network creation behavior, now I am more intrigued to investigate the service further.
IP investigation
I can perform some OSINT using various tools available on this IP to find out more information. I can use AbuseIPDB or Greynoise or any other investigation tools out there. Since I myself performed the attack here, I will be skipping this step.
Observe chain of events
Since the service created an outbound connection to the related IP, I can filter accordingly on the discover tab.
event.code: 3 and winlog.event_data.DestinationIp: <IP>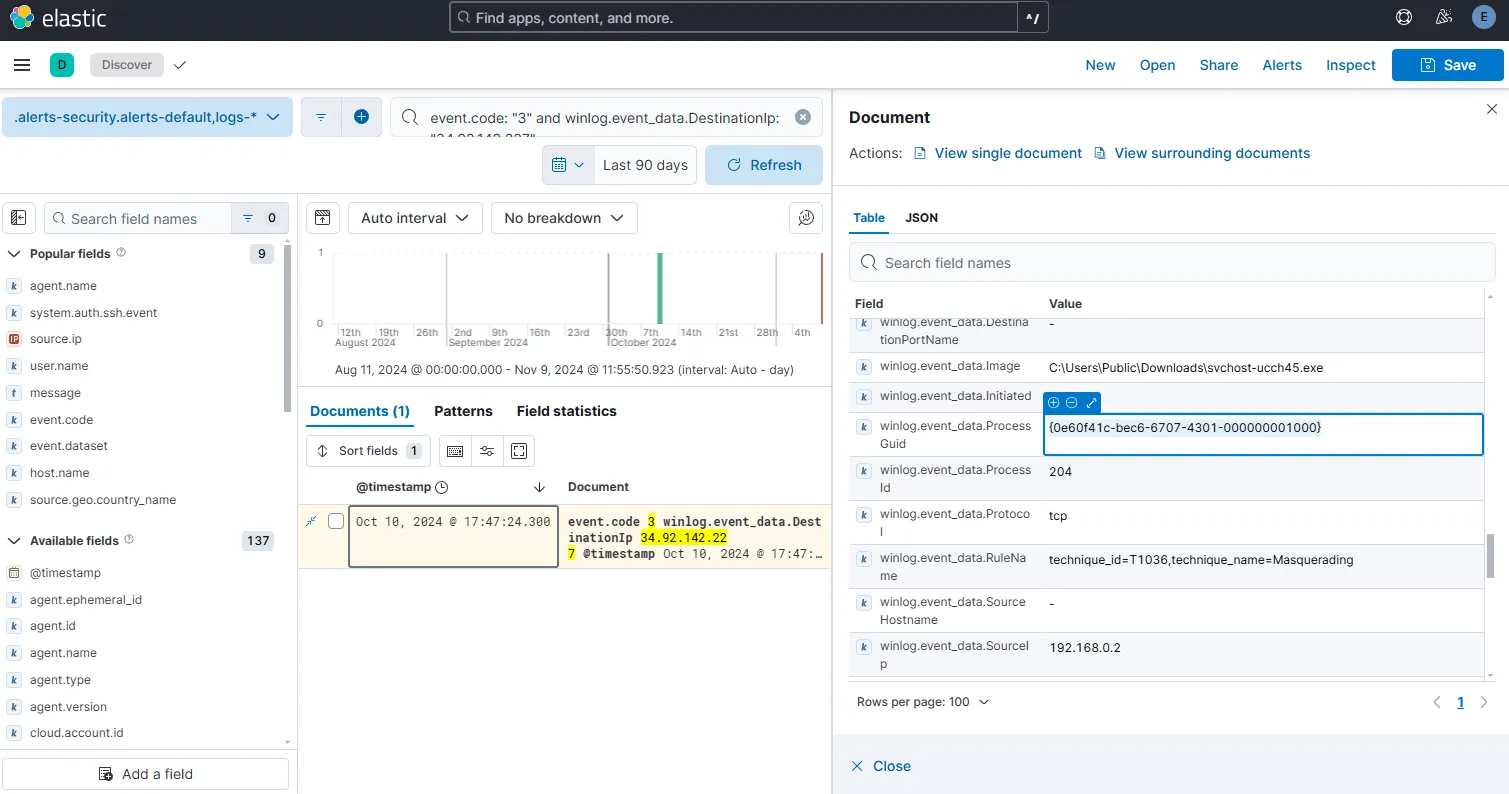
I can see that the network creation event took place on Oct 10, 2024 @ 17:47:24.300. I am copying the ProcessGuid and querying with this value again.
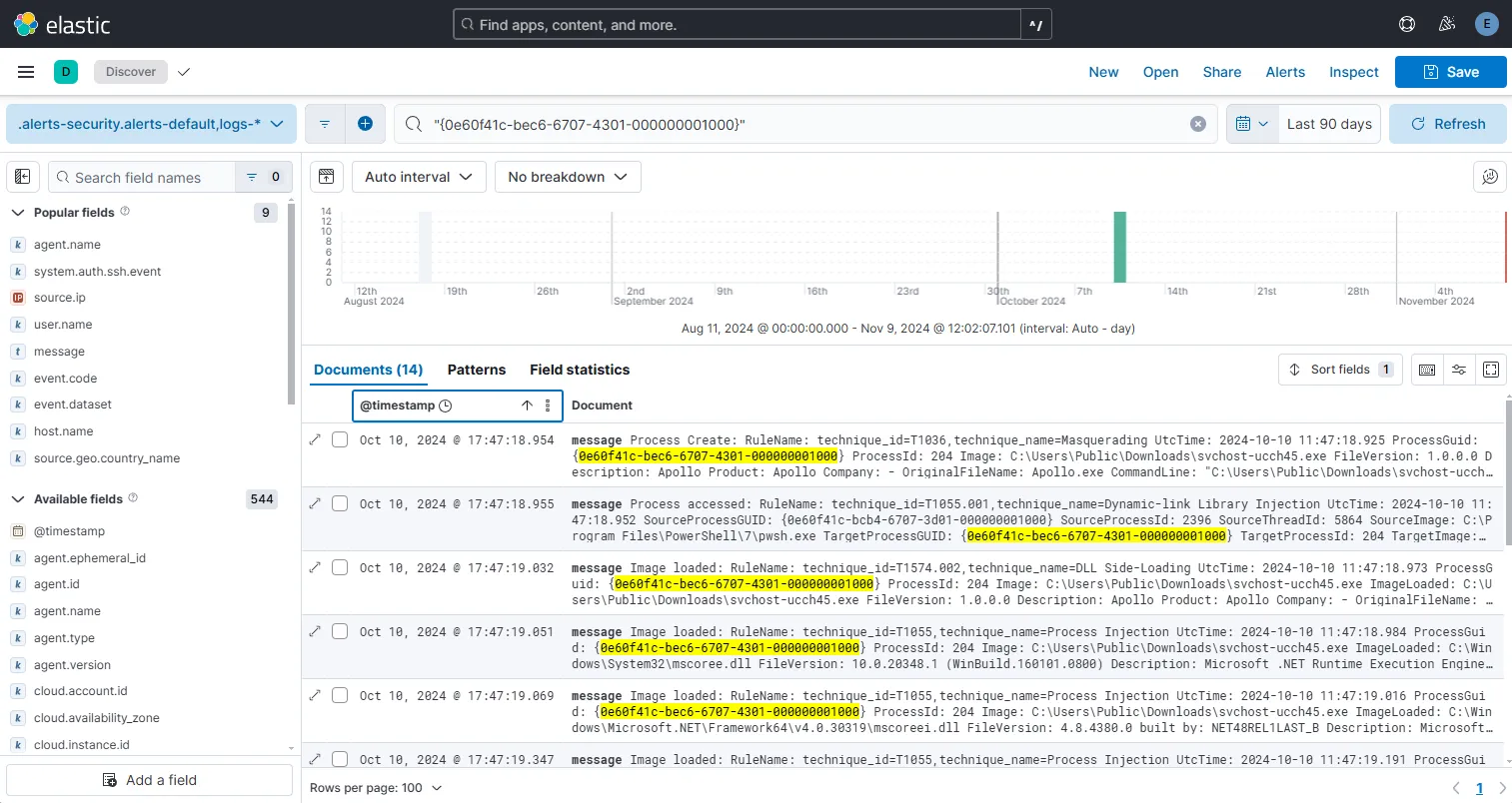
This time I find 14 records. By opening the first record, I can see that it is a Process create event Event ID 1 which was the execution of the actual executable. I can back trace the event by following the ParentProcessGuid and find out more about previous file/network activity and the parent PIDs with a focus on finding out the origin.
By sorting the records I find from old to new by timestamp, I can determine the start and end of the chain and the total duration of the event also. Let’s start creating a reference note to start tracking and correlating the events.
File: svchost-ucch45.exeFile Hash:SHA1=E4FD5B1484BDA33CC0121CD222C0A83E3F44F774,MD5=3A0D570A0F2ED6EA39523E111E15FD2E,SHA256=07753DF198B3149B461B5E2BD8B96FF7AFB7B072AF2541AB323E54805DFFD6EA
Timeline --
PARENT PROCESS: powershell
Oct 10, 2024 @ 17:38:28.826 -- Process created pwsh.exe(Powershell) PID 2396 from parent process explorer.exe(Windows File Explorer)Oct 10, 2024 @ 17:44:42.412 -- File Created svchost-ucch45.exe under C:\Users\Public\Downloads\Oct 10, 2024 @ 17:44:42.554 -- File Executable Detected C:\Users\Public\Downloads\svchost-ucch45.exe (File hash noted above)Oct 10, 2024 @ 17:47:18.954 -- Process Created with PID 204, OriginalFileName: Apollo.exeOct 10, 2024 @ 17:47:18.955 -- Process accessed Target PID 204
PROCESS: svchost-ucch45.exe
Oct 10, 2024 @ 17:47:24.300 -- Network connection detected from PID 204, TCP, Destination 34.92.142.227 Port 80To look for addition processes that might have been created from this process, I am going to search for parent process ID 204.
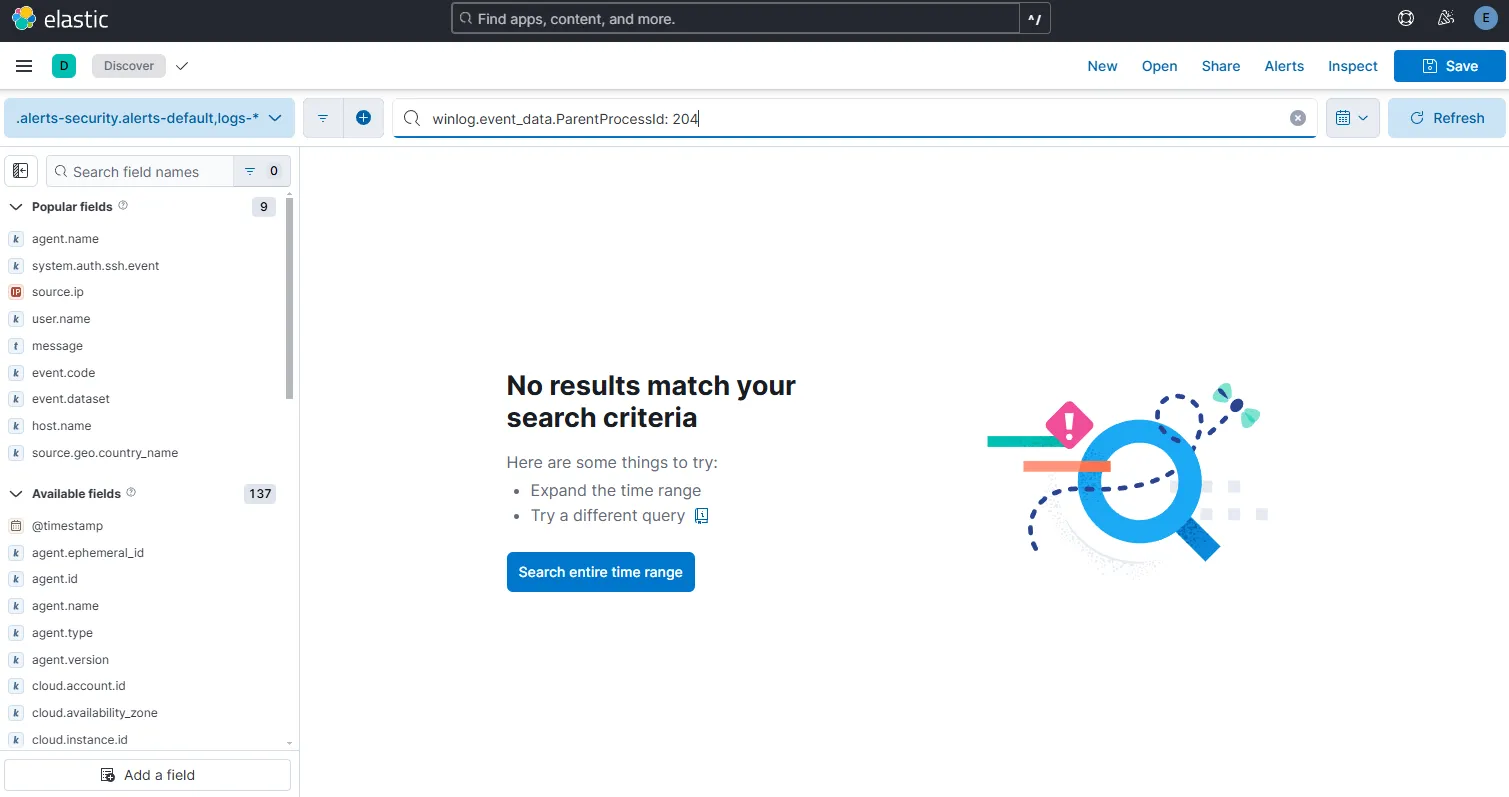
I see no results, meaning that there was no child process created from svchost-ucch45.exe.
Observe activity
Eventually after a bit more investigation, one might find the passwords.txt file being compromised. Network related data and endpoint telemetry can help us find the Mythic C2 communication with the host in order to find such cases. That’s why it is always a good idea to collect both endpoint data and network data. For this project, I cannot carry out this step as network telemetry is not collected.
Update Mythic Alert for osTicket
Let’s go to Rules under Security and select Detection Rules. Select the rule Mythic Agent Detected - Apollo C2. I would want a ticket to be generated each time a Mythic C2 activity is detected. For that, I am adding the pre-made message as body and creating an webhook action for this rule.
I am running the mythic c2 service again on my windows machine to generate alerts.
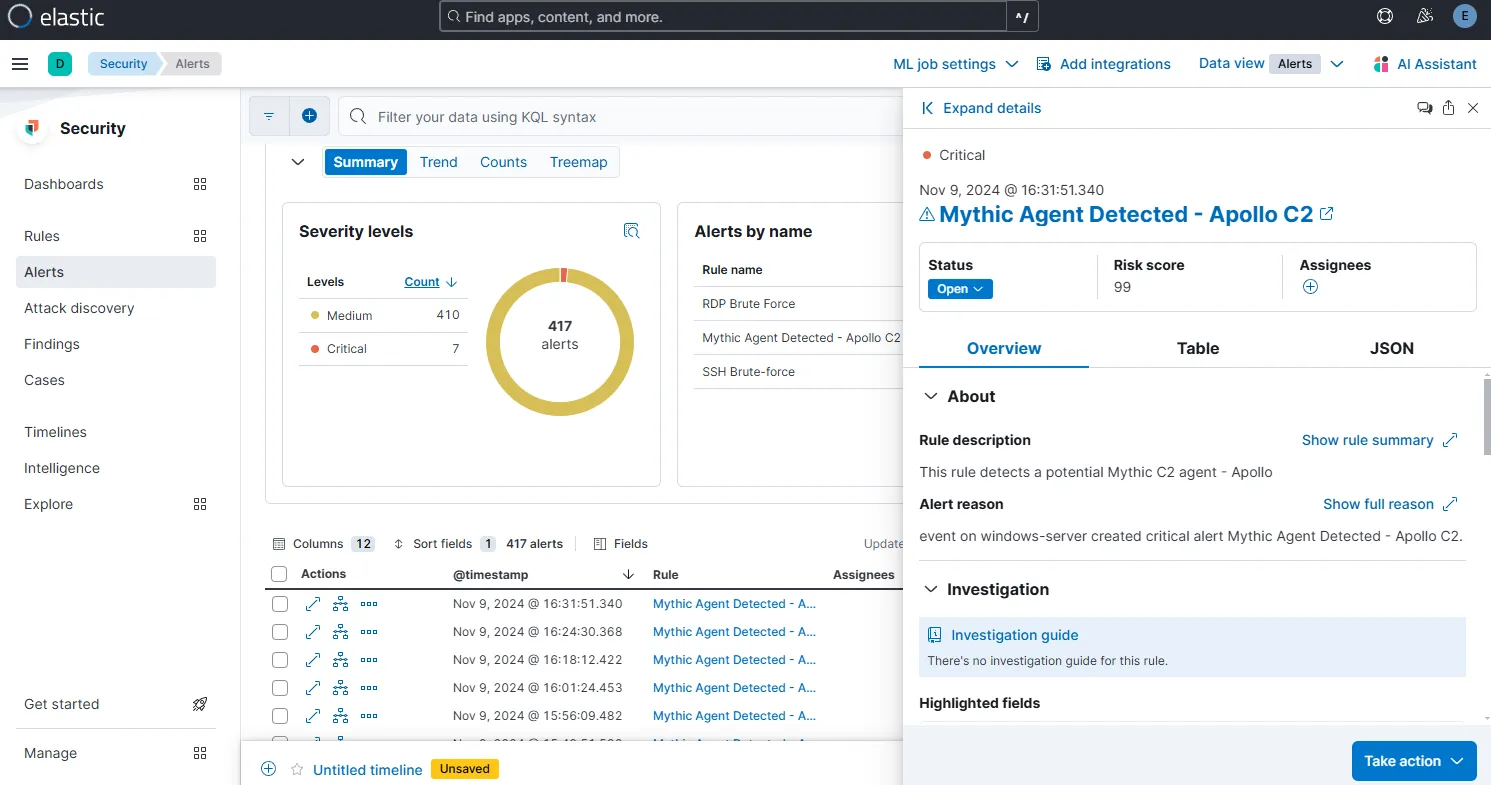
If I now go to the osTicket Agent Panel, I can see the tickets generated against the alerts.
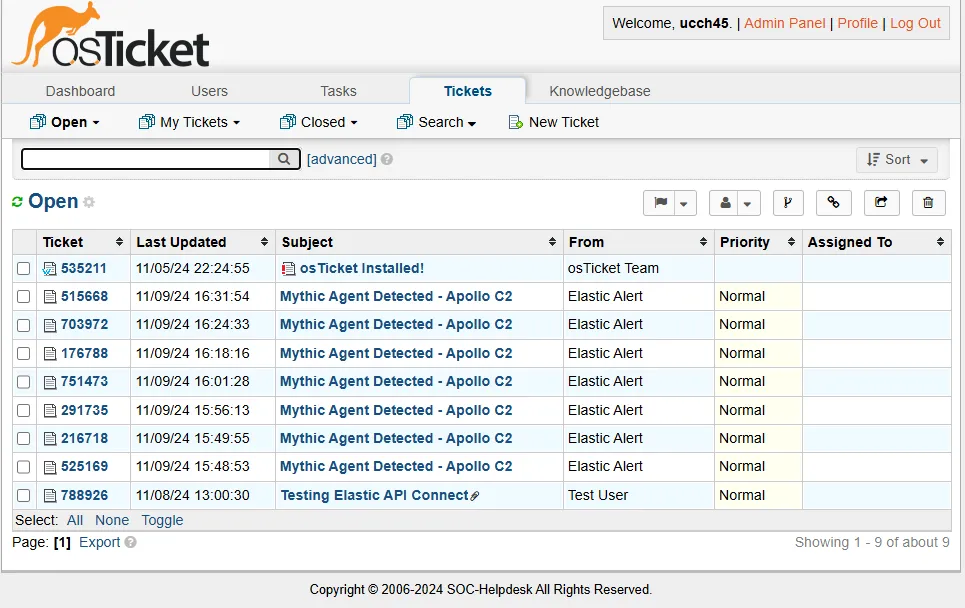
By opening the ticket, now I can assign the ticket to someone. That person can go ahead to resolve the ticket and post replies against the ticket as necessary.
Typically, a Mythic C2 operator (the attacker) sends a command via an existing C2 session. This will generally be captured in the packet layer (encrypted) but some exceptions apply in cases of spawning a powershell session, command pormpt or loading DLLs. For example, running the command like netstat from the callback session will be encrypted and will require packet layer inspection. But if the attacker spawns a new command prompt by executing a command like shell ipconfig, this will create another process and the event telemetry will be captured on the endpoint giving us the ability to investigate the generated logs from our SIEM.